Indonesia, with its vibrant culture, diverse landscapes, and growing economy, has become an attractive destination for expatriates seeking employment.
However, working in Indonesia legally requires obtaining a work permit, known locally as an “Izin Kerja.” This guide will walk you through the essential steps, requirements, and procedures to secure a work permit in Indonesia.
Understanding the Work Permit System in Indonesia

Before diving into the application process, it’s essential to understand the work permit system in Indonesia. The Indonesian government regulates foreign workers to ensure they contribute positively to the local economy and do not take away job opportunities from local citizens.
The key components of the work permit system include:
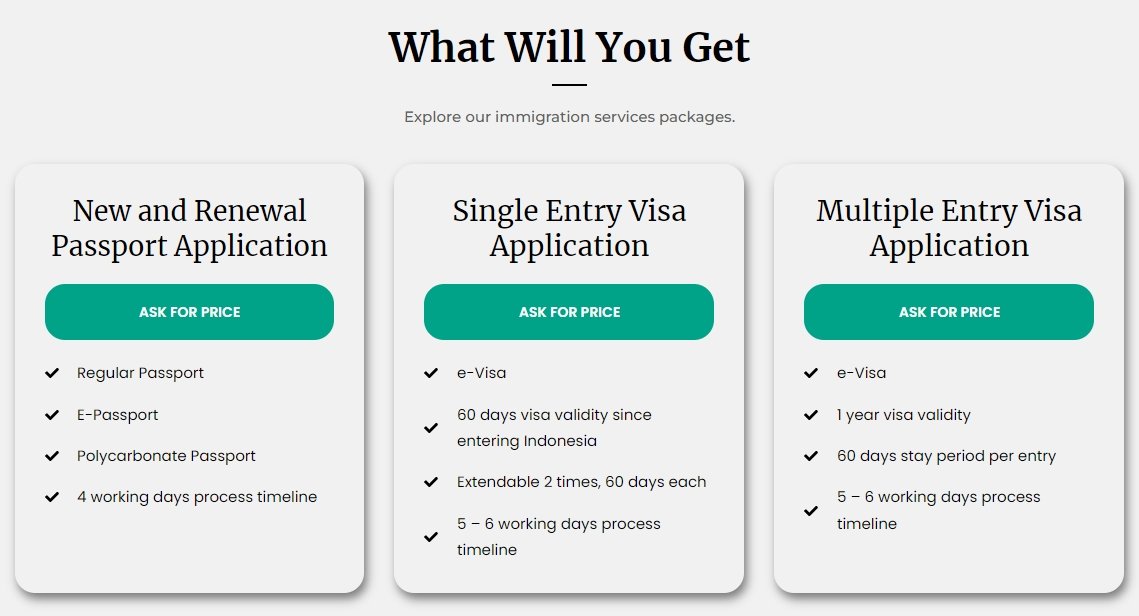
1. Limited Stay Permit (KITAS)
This is the primary visa required for expatriates working in Indonesia. It allows foreigners to stay in the country for a specified period, usually tied to their employment contract.
2. Expatriate Placement Plan (RPTKA)
Employers must submit an RPTKA to the Ministry of Manpower, detailing the need for hiring a foreign worker and justifying that no local candidates can fill the position.
3. Work Permit (IMTA)
The actual permit that allows a foreigner to work in Indonesia legally.
Requirements for Obtaining a Work Permit

Securing a work permit in Indonesia involves meeting specific criteria and submitting various documents. Here are the general requirements:
1. Employment Offer
A valid job offer from an Indonesian company is mandatory. The employer must be willing to sponsor the foreign worker’s permit.
2. Relevant Qualifications
The applicant must possess the necessary qualifications, skills, and experience relevant to the job position.
3. Health Insurance
Proof of health insurance coverage during the stay in Indonesia.
4. Clear Criminal Record
A police clearance certificate from the applicant’s home country.
Step-by-Step Process to Obtain a Work Permit
1. Securing a Job Offer
The first step is to secure a job offer from an Indonesian company. Ensure that the employer is willing to sponsor your work permit.
2. Expatriate Placement Plan (RPTKA)
The employer must submit an RPTKA to the Ministry of Manpower. This document outlines the job description, duration of employment, and justification for hiring a foreign worker. The RPTKA must be approved before proceeding with the work permit application.
3. Work Permit Application (IMTA)
Once the RPTKA is approved, the employer applies for the IMTA on behalf of the foreign worker. The IMTA is the official work permit that allows the expatriate to work in Indonesia legally.
4. Limited Stay Visa (VITAS)
With the IMTA in hand, the next step is to apply for a Limited Stay Visa (VITAS) at an Indonesian embassy or consulate in the applicant’s home country. This visa allows entry into Indonesia to finalize the work permit process.
5. Arrival in Indonesia and Conversion to KITAS
Upon arrival in Indonesia, the VITAS needs to be converted into a Limited Stay Permit (KITAS). This involves registering with the local immigration office, undergoing a medical check-up, and submitting necessary documents.
6. Police Registration and SKTT
Foreign workers must register with the local police department and obtain a Police Registration Certificate (STM). Additionally, they need to apply for a Temporary Stay Permit Card (SKTT) at the local Civil Registry Office.
Important Considerations
1. Language and Cultural Barriers
While English is widely spoken in business settings, having a basic understanding of Bahasa Indonesia can be beneficial. Familiarize yourself with local customs and business etiquette to integrate smoothly into the work environment.
2. Taxation
Foreign workers in Indonesia are subject to local tax laws. Ensure you understand the tax obligations and comply with the regulations to avoid legal issues.
3. Renewal and Extension
Work permits and KITAS are typically valid for one year and can be renewed. Start the renewal process well in advance to avoid lapses in your legal status.
4. Dependents
If you plan to bring your family, ensure they have the appropriate dependent visas and permits. Children may need to apply for student visas if they intend to attend school in Indonesia.
Common Challenges and Solutions

1. Complex Bureaucracy
Navigating the Indonesian bureaucratic system can be challenging due to its complexity and frequent changes in regulations. Working with a reputable visa agent or legal consultant can help streamline the process and ensure compliance.
2. Document Preparation
Ensure all documents are prepared accurately and meet the required standards. Incomplete or incorrectly filled applications can result in delays or rejections.
3. Cultural Adaptation
Adapting to a new culture can be challenging. Engage with local colleagues, participate in cultural activities, and be open to learning about Indonesian customs to ease the transition.
Obtaining a work permit in Indonesia involves navigating a series of steps and meeting specific requirements. While the process can be complex, understanding the system and preparing thoroughly can help ensure a smooth application.
View this post on Instagram
By securing the necessary permits and adhering to local regulations, you can enjoy a fulfilling professional experience in one of Southeast Asia’s most dynamic countries.
Remember, staying informed and seeking professional assistance when needed are key to successfully obtaining and maintaining a work permit in Indonesia.